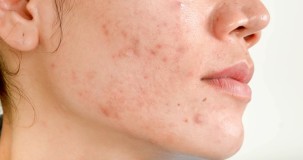
 Symptoms
Symptoms
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Baby
Baby
 Baby
Baby
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Benefits
Benefits
 Benefits
Benefits
Can eye stroke go away on its own? Eye stroke, also known as retinal artery occlusion, may not go away on its own. It requires immediate medical attention to minimize vision loss and prevent further damage.
Introduction
Eye stroke, also known as retinal artery occlusion, is a condition where the blood flow to the retina is blocked, resulting in sudden vision loss. It can be a frightening experience for individuals who face this situation. One of the common questions that arise is whether an eye stroke can go away on its own without any medical intervention. In this article, we will explore this issue further.
Understanding Eye Strokes
Eye strokes occur when a clot or debris blocks the retinal artery, leading to the interruption of blood flow to the retina. The retina is responsible for converting light into visual signals that are sent to the brain, enabling us to see. When the retinal artery is blocked, it can lead to significant vision impairment or even complete loss of vision in the affected eye.
Evaluating the Possibility of Self-Resolution
Eye strokes are considered a medical emergency, and immediate treatment is necessary to minimize potential vision damage. Unlike some other types of strokes, eye strokes do not typically resolve on their own. The blockage in the retinal artery often requires medical intervention to restore blood flow and prevent further complications.
Treatment Options
If you or someone you know experiences an eye stroke, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Ophthalmologists or retina specialists are the medical professionals who specialize in treating this condition. They can evaluate the severity of the occlusion and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Primary Treatments for Eye Strokes
The two primary treatments for eye strokes are:
1. Intra-arterial thrombolysis: This procedure involves injecting a clot-dissolving medication directly into the blocked retinal artery. The goal is to dissolve the clot, restore blood flow, and potentially improve visual outcomes.
2. Retinal laser therapy: In this procedure, a laser is used to create tiny burns on the retina. These burns help in creating new blood vessels, bypassing the blockage, and re-establishing blood flow to the affected area.
Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention plays a critical role in the treatment and prognosis of eye strokes. Timely administration of medical procedures can potentially improve the chances of restoring vision and preventing long-term complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is unlikely that an eye stroke will go away on its own without medical intervention. Prompt medical attention and appropriate treatments are necessary to restore blood flow, salvage vision, and minimize potential long-term damage. If you or someone you know experiences sudden vision loss, it is crucial to seek immediate medical care to increase the chances of a positive outcome. Remember, time plays a vital role in the treatment of eye strokes, so act swiftly to protect your vision.
Yes, in some cases an eye stroke can go away on its own. The recovery process can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the eye stroke. It is important to seek medical attention to determine the appropriate treatment plan.
2. What are the symptoms of an eye stroke?The symptoms of an eye stroke may include sudden blurred vision, loss of vision in one or both eyes, floaters (spots or lines in your field of vision), and pain or pressure in the eye. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
3. What are the risk factors for an eye stroke?Some risk factors for an eye stroke include high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, and a history of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, individuals over the age of 50 and those with a family history of eye strokes may be at an increased risk.
4. How is an eye stroke diagnosed?An eye stroke may be diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination, including a dilated eye exam. Your doctor may also perform imaging tests, such as a fluorescein angiography or optical coherence tomography (OCT), to evaluate the blood flow and structure of the blood vessels in the eye.
5. What are the treatment options for an eye stroke?The treatment options for an eye stroke depend on the underlying cause. In some cases, no specific treatment may be required and the symptoms may resolve on their own. However, if an underlying condition is identified, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, it will be important to manage and control these conditions to reduce the risk of future eye strokes. Other treatment options may include medications to improve blood flow or surgery to repair damaged blood vessels.
 LATEST ARTICLES
LATEST ARTICLES

At what stage in pregnancy does heartburn start?

Can a pregnancy test be wrong?

Can constipation hurt the baby during pregnancy?

Can a pregnancy test be wrong if taken too early?

Can a pregnancy test read wrong?

Are meds safe during pregnancy?

Can a UTI cause a false positive pregnancy test?

Can breasts be sore without pregnancy?

Can 2 faint positive pregnancy tests be wrong?

Can a pregnancy test change to positive after 10 mins?

Can a pregnancy test be positive one day and negative the next?

Can corpus luteum cyst cause positive pregnancy test?

Can a pregnancy be successful with low hCG?

Are pregnancy tests accurate at night?

Can a pregnancy test lie about being positive?

Are pregnancy bumps hard or soft?

Can clearblue detect 1 week pregnancy?

Are you dry in early pregnancy?

Can bananas cause heartburn during pregnancy?

Can autism be detected during pregnancy?

Can a positive pregnancy test can be wrong?

Can a pregnancy test be positive at 1 week?

Can AFE happen during pregnancy?
 POPULAR ARTICLES
POPULAR ARTICLES

Am I bloated or just fat?
Am I bloated or do I have an ovarian cyst?

Am I bloated or fat?

Are blackouts a symptom of depression?
Are blisters symptoms of diabetes?
Are blackouts a symptom of anxiety?

Are apples good for pregnancy?

Are any medications Pregnancy Category A?

Are bananas good for pregnancy?

Are baby kicks stronger at 20 weeks?